A specific type of tests, the marker tests are conducted to check for genetic and congenital disabilities in the developing baby. They are more commonly done to check the probability of the baby suffering from Downs Syndrome, Edward Syndrome, and Neural Tube Defects. These conditions are chromosomal abnormalities that affect both; the psychological and physiological development of the baby. Thus, it is essential to undergo routine health check-ups and tests during each trimester to ensure that a healthy baby is born. These tests also giveby you time to identify ways to tackle any problems if they arise. Dual marker tests and Quadruple marker tests are conducted for the same reason.

What is a dual marker test?
The dual marker test is a blood test usually conducted between the 11th and the 13th week of the pregnancy when the mother is in her first trimester. This test is also usually accompanied by an NT scan. The NT scan helps measure the fluid under the skin of the baby’s neck. Both these tests help determine whether the baby-to-be-born has any chances of being born with a chromosomal abnormality.
What is a quadruple marker test?
The quadruple marker test is a blood test usually conducted between the 15th and 20th week of the pregnancy during the second trimester. Like the dual marker test, this test is also performed to ascertain any genetic defects in the baby.
All gynaecologists highly advise undergoing these tests during every pregnancy.

What do the dual and quadruple markers tests help identify?
The screening tests help in effectively identifying pregnancies with a probability of an increased risk of the following medical conditions:
- Neural tube defects – The most common conditions under neural tube defects are spina bifida and anencephaly. In anencephaly, the brain of the baby does not develop adequately, and chances of survival of the baby are dim. In spina bifida, the spinal bones have an unusual opening that can cause damage to the nerves that control the lower part of the body. This may lead to paralysis of the legs, weakness, and an inability to control the bladder and bowel movements. A maternal serum test conducted in the second trimester of pregnancy can effectively detect this condition if it exists.
- Down syndrome – This is a chromosomal abnormality that leads to significant intellectual disability. Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused when abnormal cell division results in an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes the developmental changes and physical features of Down syndrome. It may also lead to physical disabilities such as heart defects, difficulty with hearing, and sight. A better understanding of Down syndrome and early interventions can greatly increase the quality of life for children and adults with this disorder and help them live fulfilling lives.
- Edward syndrome – Edwards Syndrome occurs due to the presence of added genetic material from chromosome 18. This extra material has an effect on the baby’s development and leads to external and internal physical defects. This condition leads to physical inabilities such as heart defects, defects in the digestive system, and growth deficiency. Most of the babies suffering from Edward Syndrome do not survive for more than an year. And those who do survive, require constant care and attention as they develop serious medical and developmental issues.
What does it mean if the results of these tests are positive?
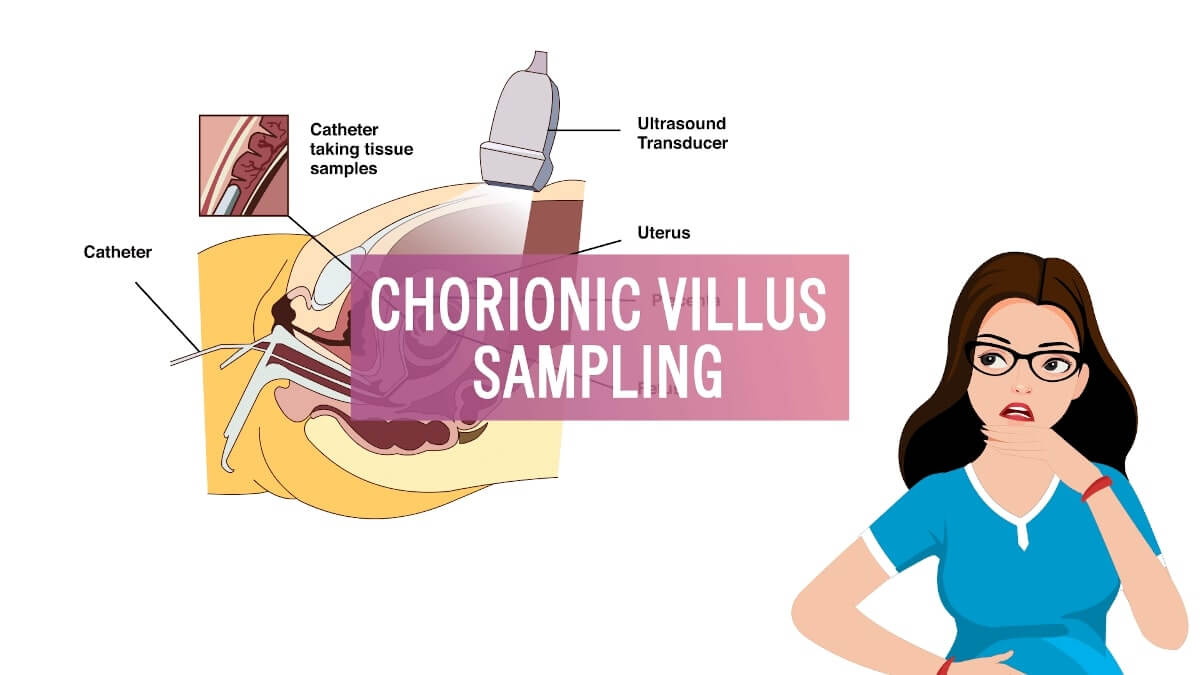
In the dual and quadruple marker test results, a mother would fall under the following categories – screen positive/high-risk category or screen negative/low-risk category. Suppose the result shows a high-risk pregnancy. In such a case, the doctor will advise you to opt for advanced and more invasive and conclusive tests like CVS sampling and amniocentesis. These diagnostic tests help in better identifying whether or not a pregnancy is affected. A chorionic villus sampling (CVS) test is usually conducted early on in the pregnancy between the 10th and 13th week of pregnancy. Amniocentesis involves the removal of amniotic fluid from the uterus which is then tested and the treatment plan is charted out accordingly.
Both the dual marker test and the quadruple marker tests go as far as to tell you whether your pregnancy is a high-risk pregnancy or a low-risk pregnancy. If the results show a high-risk pregnancy, you will need to opt for more detailed tests for a better diagnosis.
What are the steps to be taken to face a high -risk pregnancy?
If the dual and quadruple marker tests show a high-risk pregnancy, this would mean that the baby to be born has a high probability of being born with a chromosomal disorder. While there is no medical cure for this chromosomal abnormality, the child stands to benefit if provided with specialized developmental care and medical attention. Such children benefit from various therapies like speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy. A child with Downs Syndrome also requires special education and care in schools.
The dual and quadruple marker tests thus help you become aware of the problem (if any) beforehand and enable you to prepare for the same. It allows you to educate yourself and the family about the situation and equip oneself in handling such a baby. It also helps you be mentally, physically, and financially prepared for when the baby comes into your life and needs extra attention and care compared to a typical baby.
Special Thanks to Dr. Bella Bhat [MD (OB-GYN) & Fetal Medicine Consultant] for the expert advice.