In a moment, excitement is at its highest, and the second moment may drag you down under the clouds of anxious thoughts. You visit a doctor and learn about the tests, and you might be wondering why you have to go through a lot of medical screening and tests, as you have apparently no health issues. But thanks to advanced medical researches and trials, we can keep track of a baby’s development and a mother’s health by carrying out different tests from time to time. Also, routine Ultrasound checks are performed during a different time in each trimester during Pregnancy to have a broader idea of the baby’s development and position. You can find complete information under “Ultrasound during pregnancy” in the last section of the article.
The lab tests are mainly carried out by drawing a blood sample and collecting a urine sample.

Following is the information on what tests are mandatory in each trimester-
First trimester tests (Week 1 to week 12)
During the first trimester of pregnancy, the expectant mother’s body is changing at a faster pace and gearing up for the upcoming energy demands. Many physical and emotional changes take place in her body. Following is the list of mandatory tests performed during the first trimester:
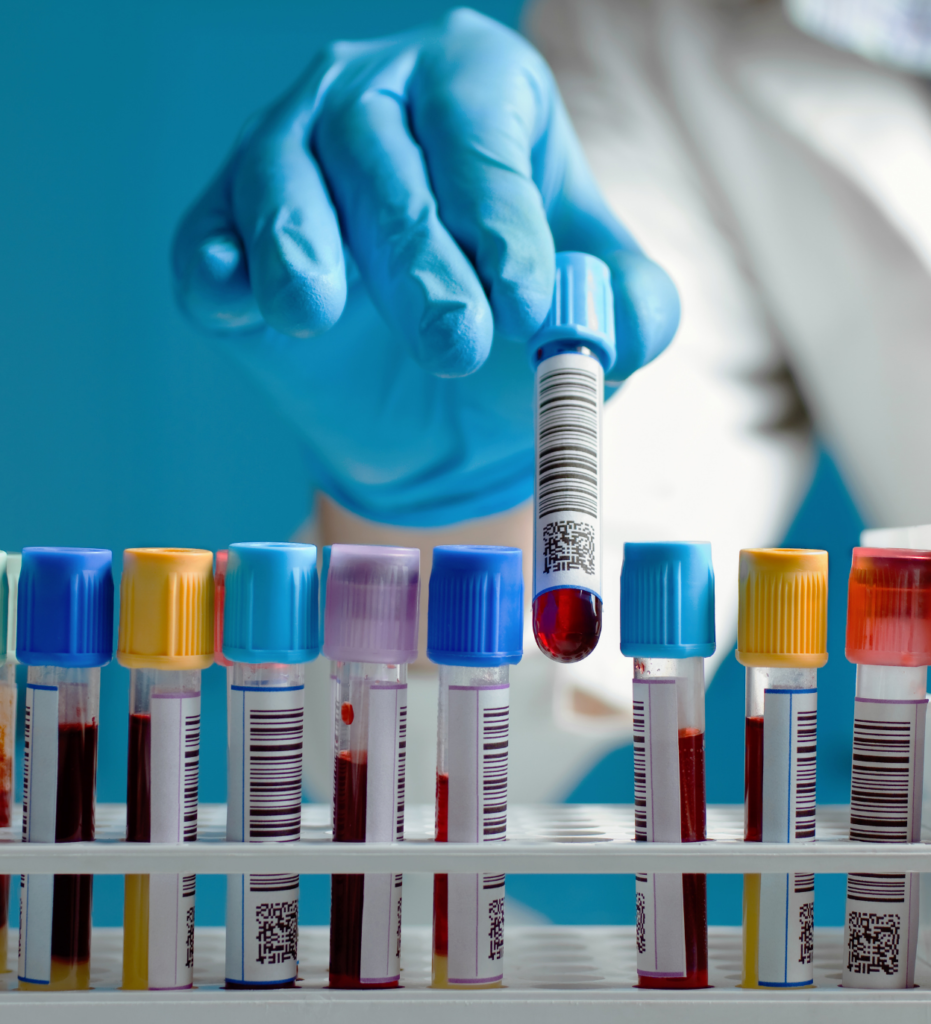
Routine Blood tests
How is the sample collected?
These tests are performed by taking blood samples from the vein on the individual’s arm.
What tests are done?
1. CBC count (Complete Blood Count) – This test is done to get information about different types of cells present in the blood. It consists of Red Blood Cell count (RBC count), White Blood cell count (WBC count), and platelet count.
Why it is necessary- It helps to evaluate overall health and get information about any active infections. Knowing hemoglobin and iron values is crucial in finding out whether the mother is suffering from anemia. If found suffering, proper supplements can be started right away. WBC values show infection status. It is usually associated with other symptoms also. If found elevated, the doctor can decide on what treatment is needed.
2. Blood Group – This test checks the blood group type such as type A, B, AB, or O.
Why it is necessary- During childbirth or other emergency circumstances, knowing a blood group beforehand is essential if blood transfusion becomes necessary.
3. Rh Factor test – This test is performed to check the rhesus factor, a protein present in the blood cells.
Why it is necessary- If the protein is present, the blood is Rh-positive, and if absent, it is termed the Rh-negative blood group. If the mother is negative and the baby is positive for Rh factor, antibodies develop that can be fatal for the fetus.
Routine Urine and urine culture tests
How is the sample collected?
A urine sample tells a lot about internal health status and is non-invasive. A fresh urine sample is used for analysis.
What is checked?
- Presence of RBC -red blood cells and WBC-white blood cells for active urinary tract infections.
- Glucose level to screen for gestational diabetes status.
- Proteins levels in the blood-Higher levels indicate severe preeclampsia complications.
- A urine culture test checks the presence of bacteria and urinary tract infections. Historically, according to researchers, Urinary tract infections have been found to decrease IQ in a fetus.
Thyroid test – The thyroid gland is a tiny gland situated near the voice box in our throat. The tiny gland releases a powerful hormone called thyroid hormone indicated by TSH and Free T4. This hormone regulates the entire body’s metabolism. As expectant mothers’ needs will increase multifold, it is necessary to check the levels in the beginning and at regular intervals as well. This test is done to check the level of thyroid hormones in the blood.
Why it is necessary?
Low hormone levels affect fetal metabolism and fetal brain development. High levels can lead to miscarriage and other complications.
How is the test done- A blood sample is taken to check the TSH and free T4 level.
Gestational Diabetes (GDM) screening- Insulin is the hormone that regulates our body’s glucose availability and use. Pregnancy, obviously a stage where glucose requirements may increase in leaps and bounces. Our Indian, mainly vegetarian diet has lots of simple carbohydrates in it. Furthermore, women, especially those whose parents already have diabetes, can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
Why is it necessary?
High sugar levels in the blood for a long time can damage internal organs, especially kidneys, and underutilization by the body may make an expectant mother feel low in sugar, despite having free sugar in the blood. There are chances the baby is overfed because of that, and an overweight baby can create further complications in delivery.
Blood sugar level test – First, there is a screening test, wherein RBS -Random blood sugar is analyzed from a blood sample. This test is done to check sugar levels in the blood.
If found more than the normal range, A Glucose tolerance test is carried out. A pregnant mom consumes a sugar solution, and blood is drawn at different intervals to determine how the body reacts to this sugar load.
However, the HbA1c test is quite accurate in screening and is carried out along with the RBS test.
This test is generally done after 24 weeks or in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Vitamin B12- Vitamin B12 is necessary for brain and neurological development. Considering Indian (Especially vegetarian diet), there are more chances of vitamin B12 deficiency.
Why is it necessary?
Any deficiency may lead to severe complications like Spina bifida or Faulty development of the baby’s nerves and brain.
Vitamin D- this test is performed by taking blood samples from the vein of the pregnant women’s arm.
Why is it necessary?
Any deficiency may lead to weak bone development and small stature in newborns.
Tests for checking infection status
- Hepatitis B antigen test – Hepatitis is a liver infection and can be passed to the fetus from the infected mother. It can create severe complications for the developing baby.
- HCV test – This test is performed to check Hepatitis C infection. Hepatitis C can be passed to the fetus and lead to a severe illness in the infant.
- Rubella Infection (German measles) – In this test, the expectant mother’s blood is checked for the presence of any antibodies present in the blood. If it happens during the first few months of pregnancy, there are chances of severe congenital disabilities such as mental retardation and improper functioning of eyes and ears. If not, there are chances of contracting the infection in the future.
- HIV infection – AIDS is not a new term for any of us, and it is indeed a lethal infection that must be screened thoroughly for an expectant mother. HIV infection attacks the body’s immune system, passing to the fetus from the mother.
- VDRL test / sexually transmitted disease test – Venereal Diseases Research Laboratory test is done to check syphilis infection. It is a bacterial infection that can cause complications during Pregnancy and transmitted to the fetus during pregnancy.
Tests for checking the parenteral blood group compatibility

It is crucial to check the blood groups compatibility of mother and father’s blood groups. Since if they have incompatible blood groups, there are chances children can have thalassemia.
Tests for 2nd trimester (Between 11-13 weeks of gestation)
The second trimester is the best trimester of the pregnancy journey since a mother-to-be can still move around and still enjoy the kicks and hiccups of the baby.
A urine infection test is carried out in this trimester to ensure the expectant mother’s infection status.
Genetic disorder screening is usually suggested for expectant mothers. Still, diagnostic tests are to be done only for high-risk patients.
Dual marker test/ maternal serum screening– PAPP-A (Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A screening) is done to screen any chromosomal abnormalities. A pregnant woman can be considered high-risk for genetic disorder testing if she is more than 35 years old, has a family history of such genetic disorder, or has abnormal screening test results. When a maternal result shows abnormal results, further tests are carried out.
Test for Down’s syndrome or other genetic disorders like trisomy 13, trisomy 18 are as follows:
Amniocentesis – Amniotic fluid or fluid surrounding the baby is tested.
Cell-free fetal DNA testing in which the maternal blood is analyzed to determine any genetic abnormality in the fetus.
Visit 3- The third trimester.
This trimester is crucial for both mom and baby. The baby is increasing in size and now shaping up exactly as a little human body inside the womb. Growing demand for nutrients may alter bodily metabolism, and the body triggers more insulin production. At this stage also for proper development of the baby, it is necessary to carry out Glucose screening- glucose tolerance test and thyroid screening, which is mentioned in the previous section.
Group B Streptococcus test is also carried out at this stage to determine the infection status in the body. Streptococcus group B is present in almost all healthy women’s vagina and rectum. Although a rare occurrence, If a pregnant mother is +ve, the infection can pass to the baby during labor and may produce diminished IQ levels in offspring.
Ultrasound during Pregnancy
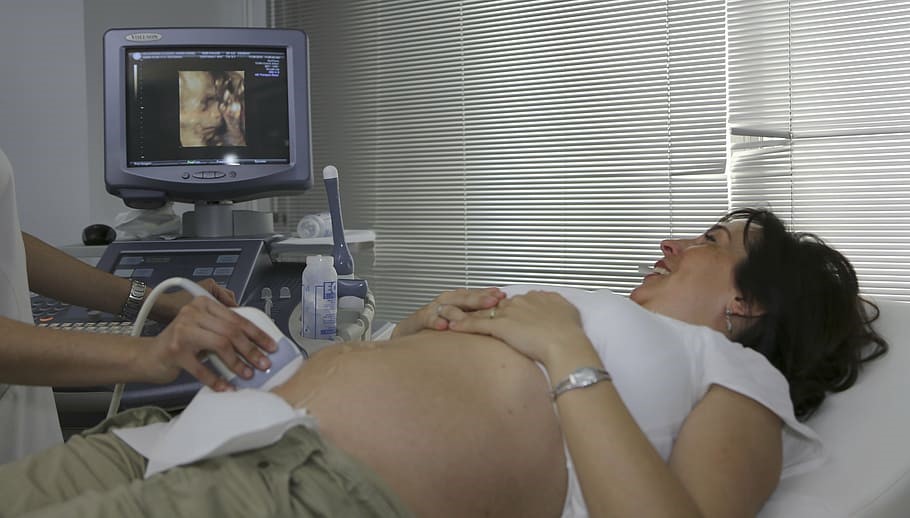
Ultrasound is the Obstetrician’s third eye and helps optimize the Pregnancy outcomes for the mother and the baby.
Routinely advised ultrasounds are as below :
1. Early scan: Few weeks after a woman misses her periods. This scan confirms Intra-uterine Pregnancy, demonstrates heartbeat, bleeding, number of fetuses, and rules our ectopic Pregnancy (Pregnancy outside the uterus- which can be life-threatening for the mother).
2. 11-13 weeks (NT-NB scan) sonography: This is an important USG to look for chromosomal and genetic abnormalities markers. It also diagnoses early and severe fetal defects.
3. Anomaly scan/19 weeks USG: This is the most crucial sonography in Pregnancy as it checks for the baby structures from head to toe. If there is some abnormality of any kind in the fetus, the chances of diagnosing it on this ultrasound are highest.
4. Growth scans 28 weeks/34-36 weeks – This ultrasound is called a fetal wellbeing scan as it checks if the fetus is growing fine, there is enough amniotic fluid, and whether it is receiving proper blood supply from the mother.
These are the basic ultrasounds of Pregnancy. The frequency of sonography may increase if there are maternal or fetal high-risk factors, and your gynecologist may guide you through it.
Pregnancy is a one-lifetime event, and every pregnant mom wants to make it memorable and enjoyable. Doing regular doctor visits and counseling on food habits, ultrasound scans, and performing these mandatory tests can undoubtedly put you, your partner, and the bundle of joy in a perfect pleasure spot.
Special thanks to Dr. Pooja Lodha (MBBS, DNB – Obstetrics & Gynecology) for the expert advice.