Fluid-filled sacs or pockets on the surface or inside an ovary are known as ovarian cysts. On each side of the uterus, two ovaries perform ovulation functions during the monthly menstrual cycles during the reproductive stage of a woman’s life. Many women are known to have ovarian cysts most often than not; the cysts are known to cause little or no discomfort and other health complications. Physiological Cysts are harmless and disappear within a few months, usually without treatment.
However, cysts that persist or increase in size can give rise to health symptoms. It is thus, imperative to get yourselves a pelvic examination or sonography regularly to diagnose any problems in time and steer clear of complications.
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
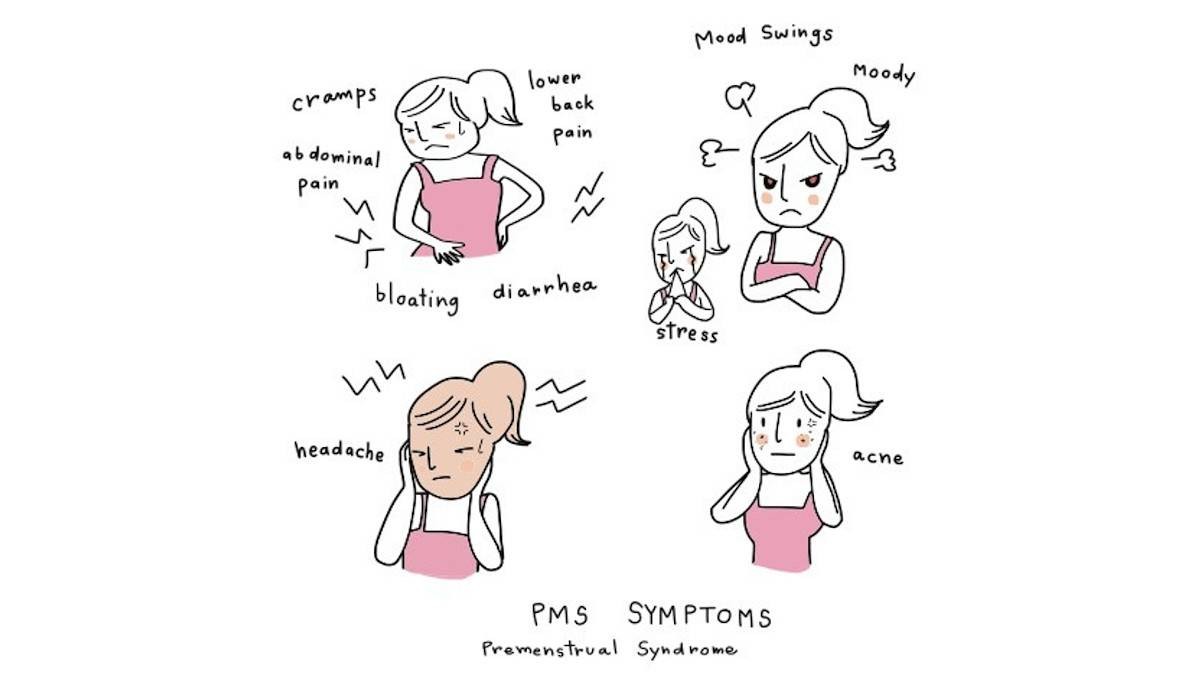
Most ovarian cysts do not lead to any symptoms. Still, those that are harmful to the health usually tend to show vague symptoms – sometimes mild and sometimes severe. The most common symptoms seen in cases of ovarian cysts are as follows:
- Bloating
- A feeling of heaviness and fullness in the abdomen
- Pelvic pain
- Painful bowel movements
- Painful intercourse
- Pain in the thighs or the lower back
- Lower abdominal pain
- Menstrual problems – pain & irregularity
- Frequent urination
In some more severe cases, there is a sudden and intense sharp pain in the lower abdominal area, sudden pain in the abdomen or the pelvis, along with fever and vomiting.
If you have been experiencing any of these symptoms frequently, you need to consult a gynecologist without further delay.
Most ovarian cysts are benign and go away naturally, while some cancerous cysts may require medical intervention. Cases where ovarian cysts become a significant concern are:
- Ruptured cysts – Ruptured cysts are very rare but can cause severe pain and internal bleeding. The bleeding also increases the chances of getting an infection and may even prove fatal if left untreated.
- Ovarian torsion – This problem arises when either of the ovaries twists or turns from it’s original position due to a large cyst around. This results in the blood supply being cut off and may lead to damage or death of the ovarian tissue if left untreated.
It is always a smart move to consult a doctor when you experience any ovarian cyst symptoms and get yourself examined to ensure no complications. The doctor will advise you to get some tests done, including tumor markers CA 125 & Imaging like ultrasonography, CT scan, or MRI.
Special Thanks to Dr. Harshad Parasnis, (MD, DNB, FCPS, DGO, FICOG, FICS) for the expert advice.