Key facts about STDs and adolescence:
- Sexually active individuals have equal possibilities for being infected with STDs irrespective of age, gender, location, and socio-economic status
- Most of the STDs do not show any symptoms at an early stage. However, they are contagious and cause chronic serious illness in the long-term.
- Women suffer more frequently than males. Women become prone to conditions like pelvic inflammatory diseases, ectopic pregnancy and infertility due to STDs.
- Only a few infections can be successfully treated, whereas others can only be controlled, including HIV.
- Sometimes, the mother can pass the infection to the child during or at the time of birth.
Thus, it is important to understand about STDs and act sensibly in sexual life when you suspect any symptoms of having STDs.
Some Common Sexually Transmitted Diseases are:
Chlamydia:
It is the most common STDs. It can cause genital and rectal discharge, burning sensation during urination and bleeding. In most instances, it is symptom-free. However, females are more severely affected if left untreated. It can cause pelvic inflammatory diseases. It is the inflammation of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and other reproductive organs. It can also cause infertility and ectopic or tubal pregnancy. Chlamydial infections can be treated with antibiotics.
HIV:

It affects the immune system and causes AIDS. This is a condition where one’s ability to fight against infections gets depleted drastically and becomes prone to multiple infections. It can also cause a certain form of cancer.
HPV:
HPV can cause genital and rectal warts. It keeps spreading if left untreated. However, it can remain dormant and come back after years. The most serious concern of HPV infection is cervical cancer. Pap smear test will help to identify HPV infection. Vaccines are also available for HPV protection.
Gonorrhea:
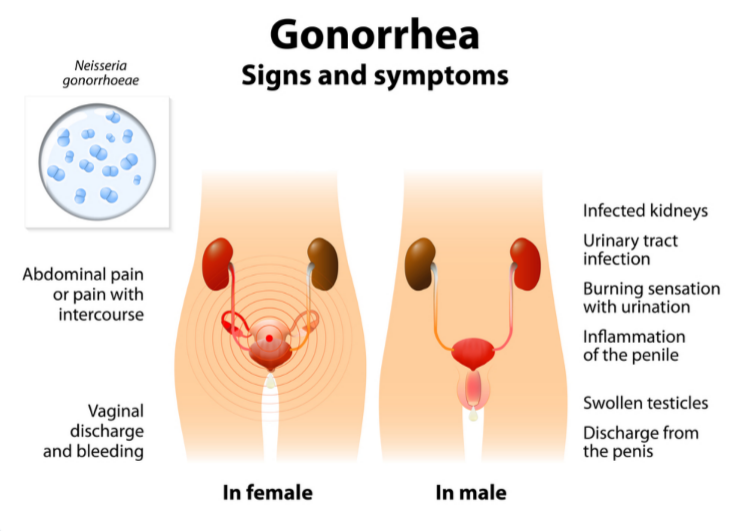
It causes discharge from the genital and rectal tract, difficulties in urination and bowel movements. In the female, it can cause serious illness like pelvic inflammatory diseases, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility. Gonorrhea can be treated with antibiotics.
Syphilis:

Symptoms begin with painless ulcers on the genital tracts followed by extremely painful rashes. If left untreated, Syphilis can affect the heart and nervous system. It can be treated with antibiotics.
Genital Herpes:

It causes painful blisters in the genital tract. These blisters can recover within a week. But the virus remains dormant in the body and reacts anytime. There is no complete cure for genital herpes. Some antiviral medicines can help to keep the symptoms under control.
Thus, it is better to practice safe sex. Immediately seek medical intervention if you think you have been infected with an STD. Discuss openly with your Doctor, to treat you better.