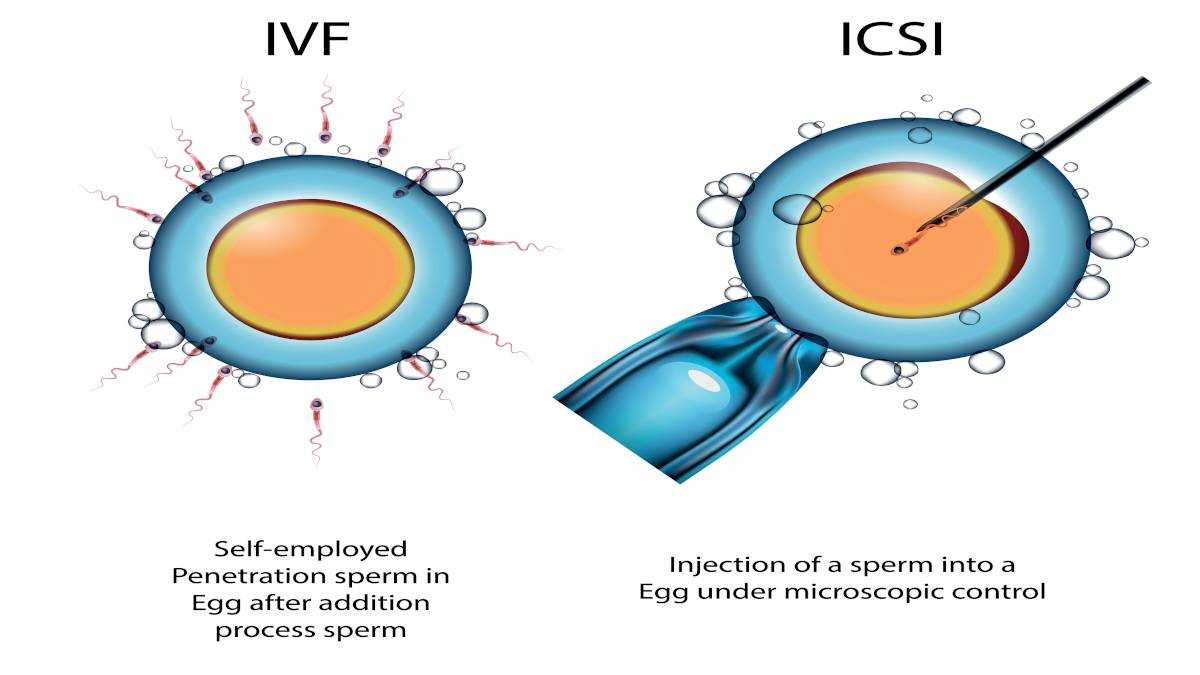
With IVF/ICSI, a woman’s egg cells (oocyte) and a man’s egg (sperms) are put together in a dish in a special fluid (culture medium) in the laboratory.

The new cell that is made when an egg cell and a sperm cell combine is called an embryo. The doctor then transfers the embryo into the woman’s uterus (womb). The embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus (implantation), where it develops and grows into a baby.
As part of the IVF process, the woman is given daily hormonal injections for 8-10 days that cause her ovaries to make several egg cells at one time than the usual one cell. The man also gives semen by ejaculation after masturbation. It has millions of male eggs-called sperms. With many egg and sperm cells to work with, several embryos are often made. The doctor will transfer one to three embryos maximum based mainly on the woman’s age and previous treatment failures, into her uterus to increase the chances of having a baby. This process of IVF/ICSI may have some extra good quality embryos that are leftover at that point in time, which can be then stored (frozen) and is known as embryo cryopreservation.

Why is embryo cryopreservation done?
There are many reasons a man and woman might choose to freeze and store their embryos:
● It can provide another chance to get pregnant if the IVF process fails for the first time as the couple will not have to go through the process of injections, multiple sonography, egg pick up by hospitalization, etc again.
● The woman can save embryos before she begins treatments, such as for cancer, which might reduce or eliminate her chances of getting good quality eggs later due to the process of chemotherapy or radiation.
● If the couple has a successful healthy baby with the first embryo, they can use the stored embryos later after a few years to have a second baby.
● They may feel it is a better option than having the extra embryos destroyed.
● The embryos could be saved and given to someone else in a donor program (noble cause) to childless couples.
● The embryos could be saved and donated for research in the field of infertility.
Embryos may be cryopreserved at any stage between day 1 to day 6 of growth (culture) after egg harvest. However, not all embryos are taken up for cryopreservation as it depends on the quality and number of embryos.
Once frozen, embryos are effectively suspended in time and all biological activity within the embryo is stopped, including cell growth or death.
When needed, embryos are slowly revived (thawed) and soaked in special fluids and they start to grow again from the stage of freezing.
How long can embryos be stored?
The frozen embryos are stored in sealed liquid nitrogen freezers having a temperature of around – 196 degrees and kept safely for many years. Extended periods of storage in liquid nitrogen have no apparent bad effects on their outcome. Embryos revived (thawed) after several years do not have any apparent bad effect on the babies born with frozen thaw process (FET CYCLE).
How safe is embryo cryopreservation?
Research has shown that freezing and thawing embryos do not harm the baby. Children born from frozen embryos have no greater rate of birth defects or health problems than children born from embryos that were not frozen.
SUCCESS RATE OF FET CYCLE IS 30-40 PERCENT OF PREGNANCY PER TRANSFER (CYCLE).
Conclusion
Since the 1980s, the embryo cryopreservation procedure has resulted in the birth of thousands of babies worldwide and has been widely used in IVF/ICSI practice. It has emerged as a very useful procedure in assisted reproductive technology.
Special thanks to Dr. Arun R. Rathi (MBBS, DGO, DNB, FCPS, DFP) for the expert advice.